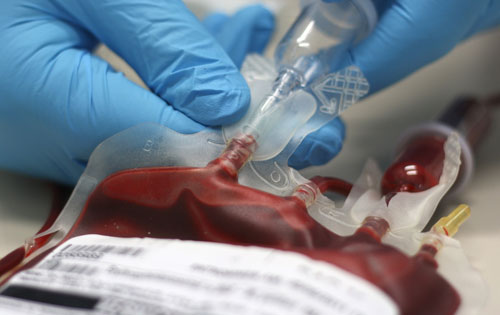
 Autologous blood transfusion is the collection and re-infusion of the patient’s own blood or blood components. Homologous, or more correctly allogenic, blood transfusions involves someone collecting and infusing the blood of a compatible donor into him/herself. Heterologous blood transfusions are those that involve someone infusing blood and its components from a different species. Withdrawal, storage and preservation, and re-infusion of blood products are carefully regulated in the health industry because infusion of infectious, old, or incorrectly matched blood could result in hospitalization and possibly death.
Autologous blood transfusion is the collection and re-infusion of the patient’s own blood or blood components. Homologous, or more correctly allogenic, blood transfusions involves someone collecting and infusing the blood of a compatible donor into him/herself. Heterologous blood transfusions are those that involve someone infusing blood and its components from a different species. Withdrawal, storage and preservation, and re-infusion of blood products are carefully regulated in the health industry because infusion of infectious, old, or incorrectly matched blood could result in hospitalization and possibly death.
What’s the difference between autologous, homologous (allogenic), and heterologous blood transfusions?
Written By
Share On


About USADA
USADA is committed to protecting clean athletes and promoting fair competition. As the official anti-doping agency for the United States, USADA provides education, testing, and resources that empower athletes to compete with integrity and confidence.
Follow Us






